This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of transferring your EPF online, exploring the benefits of such transfers, and elucidating the steps to withdraw your EPF amount.
(Isstories Editorial):- New Delhi, Delhi Jan 10, 2024 (Issuewire.com) – Navigating the EPFO Landscape for Financial Security
More on Isstories:
- AFP investigation puts a questionmark over thousands of arrests suggest TROJAN RAT data experts Fifteen Communications.
- Introducing the Best of Business YouTube TV Show: A Fresh Perspective on Entrepreneurship
- Modern day stalking epidemic impacting 5% of Australians revealed by Fifteen Communications.
- Victor Morales Hayes, MD, Renowned Orthopedic Surgeon at Elite Spine – Orthopedics
- “Billy the Bully: From the AddyBee123 Book Collection”
In the dynamic landscape of personal finance, understanding the nuances of the Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) is crucial for individuals looking to secure their financial future. This comprehensive guide delves into the various facets of EPFO, providing a detailed roadmap for contributors.
Introduction to EPFO:
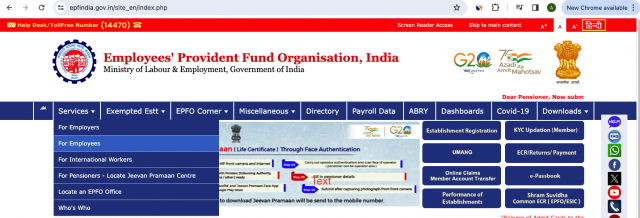
What is EPFO
The Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) is a statutory body established by the Government of India under the Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952. It serves as the principal custodian of the Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF), a social security scheme that aims to provide financial stability and security to employees in the organized sector. EPFO operates under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, overseeing the implementation of EPF, Employee Pension Scheme (EPS), and the Employee Deposit Linked Insurance (EDLI) Scheme.
Historical Evolution and Significance
Established on 4th March 1952, the EPFO has evolved over the decades to become a cornerstone of social security in India. Initially, it primarily covered industrial workers, but its scope expanded to include various sectors. The EPF scheme ensures that employees contribute a portion of their salary towards a provident fund, which, along with contributions from employers, forms a corpus that employees can access during retirement, resignation, or other specified conditions.
Mission and Objectives
The EPFO’s mission is to promote employees’ welfare by facilitating the growth of the organized sector and ensuring financial security. Its objectives include managing and overseeing provident funds, pension funds, and insurance funds, as well as administering schemes that provide financial assistance during contingencies. The EPFO plays a pivotal role in fostering a savings culture and safeguarding the economic interests of millions of employees across India.
Core Components of EPFO:
A. Provident Fund (PF):
-
Contributions and Eligibility:
- The Provident Fund (PF) is a fund where both employees and employers contribute a percentage of the employee’s salary.
- Eligibility for PF contributions includes employees in organizations with more than 20 individuals.
-
Interest Rates:
- The EPFO announces interest rates on PF balances annually. These rates are competitive and often exceed those offered by traditional savings instruments.
-
Withdrawal and Settlement:
- Employees can withdraw PF balances upon retirement, resignation, or during specific circumstances like illness.
- Settlements are processed through the EPFO’s online portal, ensuring a streamlined and efficient withdrawal process.
B. Employee Pension Scheme (EPS):
-
Structure and Benefits:
- EPS provides a pension to employees after their retirement. The pension amount is calculated based on the employee’s service period and average salary.
- It acts as a financial safety net, offering a source of income post-retirement.
-
Pension Calculation:
- The pensionable salary and service period determine the monthly pension amount.
- Continuous service of at least ten years is a prerequisite for availing EPS benefits.
C. Employee Deposit Linked Insurance (EDLI):
-
Coverage and Benefits:
- EDLI provides life insurance coverage to employees enrolled in the EPF scheme.
- In the unfortunate event of the employee’s demise during employment, the nominee receives a lump-sum insurance amount.
-
Claim Process:
- Nominees can claim the EDLI benefit by submitting the required documents, including the death certificate of the employee.
- The claims process is facilitated through the EPFO’s user-friendly portal, ensuring timely assistance during challenging circumstances.
Universal Account Number (UAN):
A. Introduction and Purpose:
The Universal Account Number (UAN) is a unique identifier introduced by the EPFO to simplify and streamline the provident fund process for employees. It serves as a revolutionary tool that unifies multiple Member Identification Numbers (MINs) allotted to an individual under different employers, ensuring a consolidated and hassle-free experience.
B. UAN Activation Process:
-
Simplified Activation:
- Activating the UAN is a straightforward process that can be done through the EPFO’s online portal.
- Employees need to provide basic details like their UAN, mobile number, and member ID such as an Aadhaar card to initiate the activation.
-
Mobile App Integration:
- The EPFO’s mobile app facilitates easy UAN activation, allowing users to access their accounts conveniently from their smartphones.
- The app ensures accessibility and empowers users to manage their UAN-related tasks on the go.
C. UAN Benefits for Contributors:
-
Consolidated View:
- UAN provides contributors with a consolidated view of their EPF accounts, eliminating the need to manage multiple IDs for different employments.
- This ensures transparency and enables contributors to track their cumulative EPF contributions effortlessly.
-
Easy Transfer and Withdrawal:
- UAN simplifies the transfer and withdrawal processes. Employees can seamlessly transfer their PF accumulations when changing jobs.
- Withdrawals, whether partial or complete, can be initiated through the UAN portal, offering flexibility to contributors.
EPF Contribution and Calculation:
A. Employee and Employer Contributions:
-
Mutual Contribution:
- The Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) operates on a contributory basis, with both employees and employers making regular contributions.
- Employees contribute 12% of their basic salary, and an equal amount is contributed by the employer, forming a cumulative 24% of the employee’s salary.
-
Voluntary Provident Fund (VPF):
- In addition to the mandatory contributions, employees have the option to contribute more voluntarily through the Voluntary Provident Fund (VPF).
- VPF allows employees to enhance their savings and build a more substantial corpus for their future.
B. Contribution Rates:
-
Fixed Rates:
- The contribution rates are fixed at 12% of the employee’s basic salary for both the employee and employer.
- These rates ensure uniformity and establish a stable framework for EPF contributions.
-
Applicability to Specific Cases:
- Certain establishments with fewer than 20 employees may have the option to contribute at reduced rates, subject to specific conditions.
- However, adherence to the standard contribution rates is common across most organizations.
C. Calculation Methodology:
-
Basis for Calculation:
- EPF contributions are calculated based on the basic salary and dearness allowance of the employee.
- Other components like house rent allowance and special allowances are not considered for EPF calculation.
-
Interest Accrual:
- The EPFO declares an annual interest rate on the accumulated PF balance, ensuring that the fund grows over time.
- Interest accrues monthly and is credited to the account at the end of the financial year.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate the intricate landscape of EPFO. From understanding the core components and contributions to leveraging online services and anticipating future developments, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for contributors aiming to maximize the benefits of their association with EPFO.
This article was originally published by IssueWire. Read the original article here.